November 2015
8
B
oards
& M
odules
or also lack long-term availability for assembly
parts and component groups. Typical applica-
tion cases for embedded NUC can be found
in MES systems and thin clients in harsh
environments, HMIs in industrial manufac-
turing, diagnostic computers in the clinical
field, POS/POI systems as well as ticketing
machines in indoor and outdoor areas, and
also in digital signage and infotainment sys-
tems for shopping malls or public transport.
Embedded NUC systems are, however, also
recommendable for applications destined for
deployment in industrial environments, as
any fieldbus can be connected via Mini-PCIe
support or internal USB extensions and Type
2 boards offer standard 2x UART/COM sup-
port. Dual LAN support additionally enables
(Industrial) Ethernet LAN to be looped
through, which eliminates the need for star
cabling on horizontally networked industrial
processing computers which in turn saves
meters and meters of cables by line topolo-
gies. With the modular embedded NUC based
on Qseven, designers have access to a highly
flexible specification with which they can cre-
ate extremely individual boards and systems
as standardized small form factor designs.
In addition, Qseven provides carrier board
design guides and established training and
workshop programs which cover all aspects
necessary for fast entry into the modular eco-
system. The high level of standardization and
the very wide availability of solutions based on
this standard, which has grown significantly
since the specification was published, increase
the overall market potential of embedded
NUC in the industrial environment as they
boost design re-use opportunities and lower
development costs. Last but not least, third
party support and long-term availability are
guaranteed. In some ways, embedded NUC is
the most specific carrier board form factor for
Qseven. But it doesn’t leave NUC developers
tied to Qseven. By taking a modular approach,
they can also opt for other computer module
form factors such as COM-Express Mini.
The high level of modularity and the com-
pact design of embedded NUC systems make
them a sort of modern successor to the for-
merly very successful PC/104 form factor.
Only the construction height of embedded
NUC is much slimmer – which is no disad-
vantage. And a further practical bonus point
is that the interfaces are mounted directly
on board. Internal cabling which – in the
case of PC/104 – was required for external
interfaces has been eliminated. Behind the
modular embedded NUC concept stands the
independent standardization board SGET,
which is committed to further developing
this vendor-independent standard. This
helps set embedded NUC systems apart from
the very heterogeneous market of industrial
Box PCs and, while support continues to
increase, brings them to a significant market
position compared to proprietary Box PCs.
At Embedded World 2015, Pentair presented
a matching case concept based on the tried
and tested Schroff Interscale concept for small
form factors. The cases can be designed flexible
and offer two standard versions for embedded
NUC: the Interscale M with perforations for
passive convection cooling and the Interscale C
with an integrated conduction cooling element.
Additionally, EMI and IP30 dust protections as
well as flexible heat conducting elements are
integrated which are variable in height to com-
pensate tolerances along the heat path, thus
guaranteeing optimal heat transfer. The eNUC-
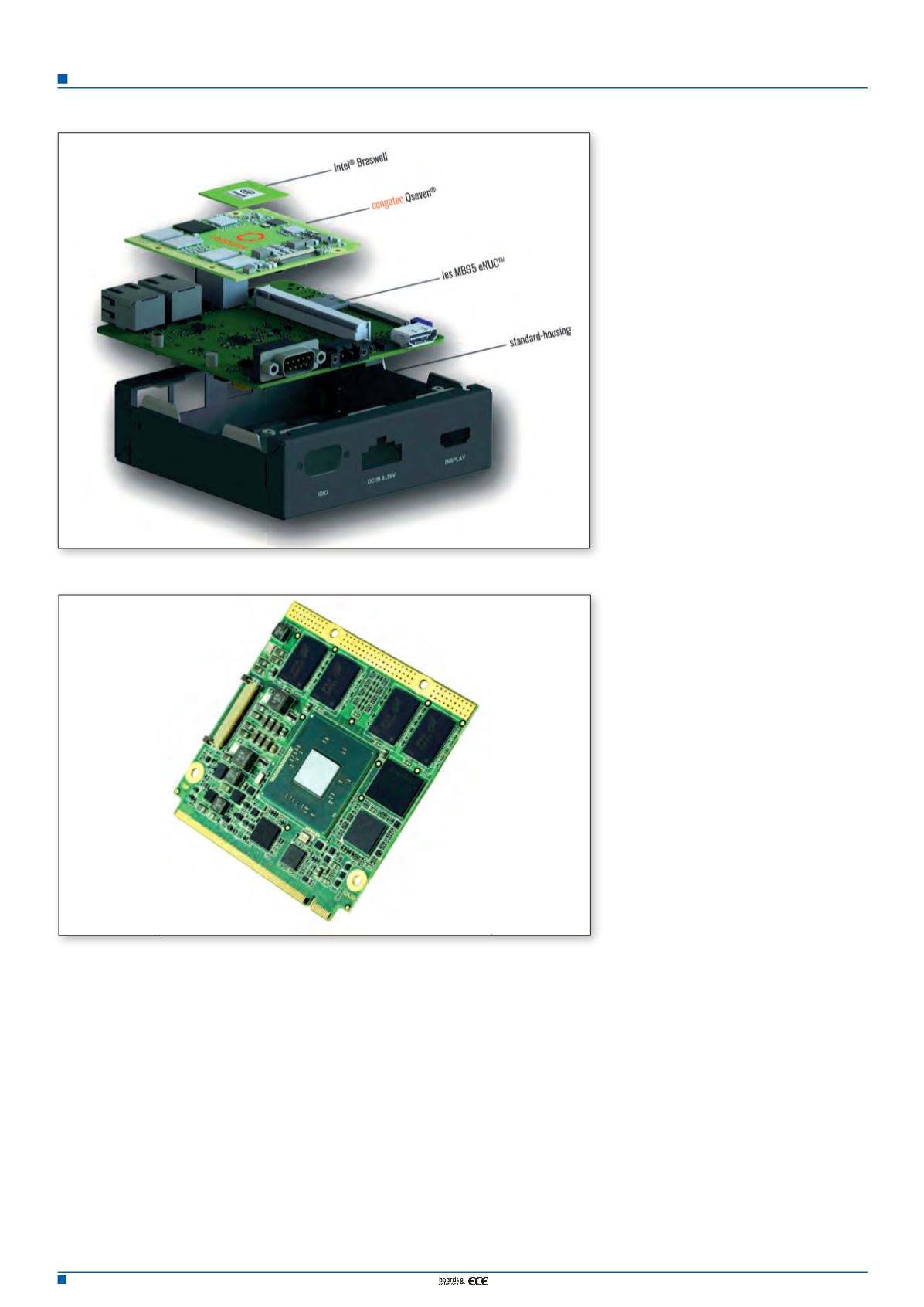
Box from ies uses the Pentair case concept and
integrates a congatec Qseven module on the
BB95 base board.
With the eNUC-Box, available not only with
AMD Embedded G-Series SoC processors
(codenamed Steppe Eagle) but now also with
Qseven modules based on the Intel Atom
processor generation E3800 (codenamed Bay
Trail) as well as Intel Pentiumand Celeron SoC
processors (codenamed Braswell), very differ-
ent applications can be catered for. Owing to
Figure 1. The ies eNUC-Box is available with congatec Qseven modules.
Figure 2. Qseven modules from congatec with Intel, AMD or Freescale processors make
the modular embedded NUC systems from ies extremely scalable.


